RESEARCH PAPERS
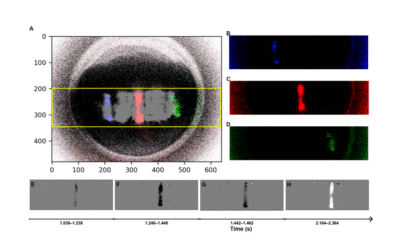
An Event-Based Opto-Tactile Skin
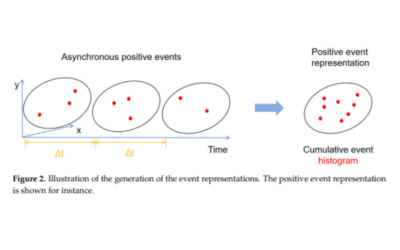
This paper presents an event-based opto-tactile skin, a neuromorphic tactile sensing system that integrates dual dynamic vision sensors (DVS) with a flexible optical waveguide to enable high-speed, low-latency touch detection over large areas of soft robotic surfaces. The system leverages sparse event streams for press localization, using clustering-based triangulation to achieve accurate tactile mapping with minimal computational overhead. Experimental results demonstrate reliable contact detection and localization across a 100 cm² sensing area, highlighting its potential for real-time, energy-efficient soft robotics applications.
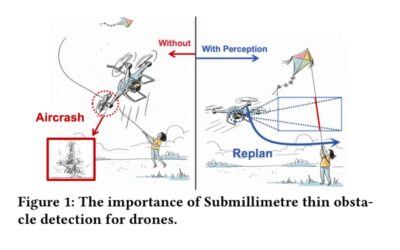
Thin Obstacle Detection for Drone Flight Safety
This paper introduces SkyShield, an event-driven framework for detecting submillimeter-scale thin obstacles—such as steel wires and kite strings—that endanger autonomous drones in complex environments. Using the high temporal resolution of event-based cameras, SkyShield leverages a lightweight U-Net and a novel Dice-Contour Regularization Loss to accurately capture thin structures in event streams. Experiment results show a mean F1 score of 0.7088 with 21.2 ms latency, making the approach well suited for real-time, edge, and mobile drone applications.
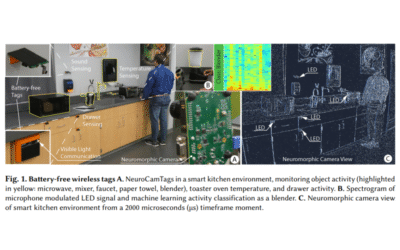
NeuroCamTags: Long-Range, Battery-free, Wireless Sensing with Neuromorphic Cameras
In this paper, NeuroCamTags introduces a battery-free platform designed to detect a range of human interactions and activities in entire rooms and floors without batteries. The system comprises low-cost tags that harvest ambient light energy and utilize high-frequency LED modulation for wireless communication. Visual signals are captured by a neuromorphic camera with high temporal resolution. NeuroCamTags enables localization and identification of multiple tags, offering battery-free sensing for temperature, contact, button presses, key presses, and sound cues, with accurate detection up to 200 feet.
Low-latency neuromorphic air hockey player
This paper focuses on using spiking neural networks (SNNs) to control a robotic manipulator in an air-hockey game. The system processes data from an event-based camera, tracking the puck’s movements and responding to a human player in real time. It demonstrates the potential of SNNs to perform fast, low-power, real-time tasks on massively parallel hardware. The air-hockey platform offers a versatile testbed for evaluating neuromorphic systems and exploring advanced algorithms, including trajectory prediction and adaptive learning, to enhance real-time decision-making and control.
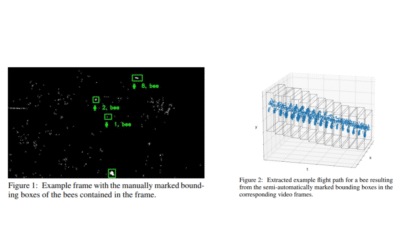
Features for Classifying Insect Trajectories in Event Camera Recordings
In this paper, the focus is on classifying insect trajectories recorded with a stereo event-camera setup. The steps to generate a labeled dataset of trajectory segments are presented, along with methods for propagating labels to unlabelled trajectories. Features are extracted using FoldingNet and PointNet++ on trajectory point clouds, with dimensionality reduction via t-SNE. PointNet++ features form clusters corresponding to insect groups, achieving 90.7% classification accuracy across five groups. Algorithms for estimating insect speed and size are also developed as additional features.
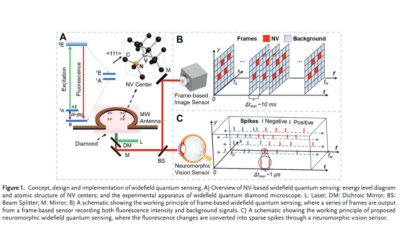
Widefield Diamond Quantum Sensing with Neuromorphic Vision Sensors
In this paper, a neuromorphic vision sensor encodes fluorescence changes in diamonds into spikes for optically detected magnetic resonance. This enables reduced data volume and latency, wide dynamic range, high temporal resolution, and excellent signal-to-background ratio, improving widefield quantum sensing performance. Experiments with an off-the-shelf event camera demonstrate significant temporal resolution gains while maintaining precision comparable to specialized frame-based approaches, and the technology successfully monitors dynamically modulated laser heating of gold nanoparticles, providing new insights for high-precision, low-latency widefield quantum sensing.
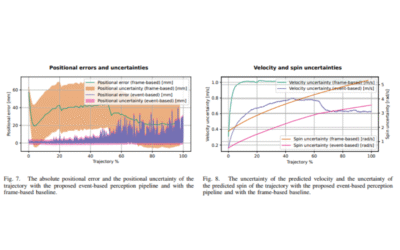
An Event-Based Perception Pipeline for a Table Tennis Robot
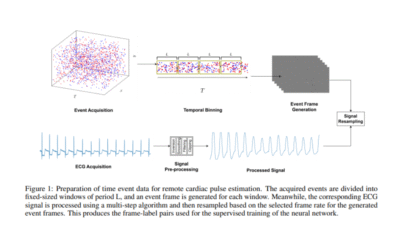
In this paper, the contact-free reconstruction of an individual’s cardiac pulse signal from time event recording of the face is investigated using a supervised convolutional neural network (CNN) model. An end-to-end model is trained to extract the cardiac signal from a two-dimensional representation of the event stream, with model performance evaluated based on the accuracy of the calculated heart rate. Experimental results confirm that physiological cardiac information in the facial region is effectively preserved, and models trained on higher FPS event frames outperform standard camera results.
Contactless Cardiac Pulse Monitoring Using Event Cameras
In this paper, the contact-free reconstruction of an individual’s cardiac pulse signal from time event recording of the face is investigated using a supervised convolutional neural network (CNN) model. An end-to-end model is trained to extract the cardiac signal from a two-dimensional representation of the event stream, with model performance evaluated based on the accuracy of the calculated heart rate. Experimental results confirm that physiological cardiac information in the facial region is effectively preserved, and models trained on higher FPS event frames outperform standard camera results.
Dynamic Vision-Based Non-Contact Rotating Machine Fault Diagnosis with EViT
In this paper, a dynamic vision-based non-contact machine fault diagnosis method is proposed using the Eagle Vision Transformer (EViT). The architecture incorporates Bi-Fovea Self-Attention and Bi-Fovea Feedforward Network mechanisms to process asynchronous event streams while preserving temporal precision. EViT achieves exceptional fault diagnosis performance across diverse operational conditions through multi-scale spatiotemporal feature analysis, adaptive learning, and transparent decision pathways. Validated on rotating machine monitoring data, this approach bridges bio-inspired vision processing with industrial requirements, providing new insights for predictive maintenance in smart manufacturing environments.
A magnetically levitated conducting rotor with ultra-low rotational damping circumventing eddy loss
In this paper, a conducting rotor is levitated diamagnetically in high vacuum, achieving extremely low rotational damping by minimizing eddy-current losses. Experiments and simulations reveal that at higher pressures, gas collisions are the main source of damping, while at low pressures, minor asymmetries in the setup cause residual eddy damping. Analytic calculations confirm that, under ideal symmetric conditions, steady eddy currents can vanish. This approach enables ultra-low-loss rotors suitable for high-precision gyroscopes, pressure sensors, and tests in fundamental physics.
BiasBench: A reproducible benchmark for tuning the biases of event cameras
In this paper, an experimental imaging flow cytometer using an event-based CMOS camera is presented, with data processed by adaptive feedforward and recurrent spiking neural networks. PMMA particles flowing in a microfluidic channel are classified, and analysis of experimental data shows that spiking recurrent networks, including LSTM and GRU models, achieve high accuracy by leveraging temporal dependencies. Adaptation mechanisms in lightweight feedforward spiking networks further improve performance. This work provides a roadmap for neuromorphic-assisted biomedical applications, enhancing classification while maintaining low latency and sparsity.
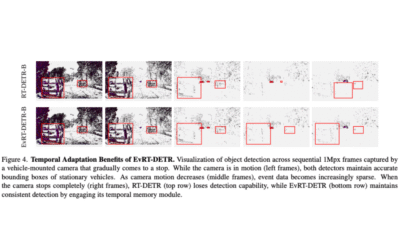
EvRT-DETR: Latent Space Adaptation of Image Detectors for Event-based Vision
In this paper, object detection for event-based cameras (EBCs) is addressed, as their sparse and asynchronous data pose challenges for conventional image analysis. The I2EvDet framework bridges mainstream image detectors with temporal event data. Using a simple image-like representation, a Real-Time Detection Transformer (RT-DETR) achieves performance comparable to specialized EBC methods. A latent-space adaptation transforms image-based detectors into event-based models with minimal architectural modifications. The resulting EvRT-DETR reaches state-of-the-art performance on Gen1 and 1Mpx/Gen4 benchmarks, providing an efficient and generalizable approach for event-based object detection.
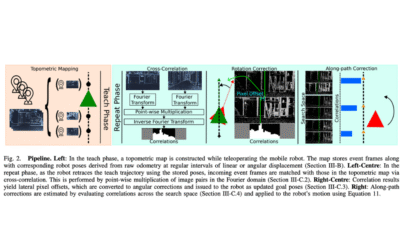
Event-Based Visual Teach-and-Repeat via Fast Fourier-Domain Cross-Correlation
In this paper, an event-camera-based visual teach-and-repeat system is presented, enabling robots to autonomously follow previously demonstrated paths by comparing current sensory input with recorded trajectories. Conventional frame-based cameras limit responsiveness due to fixed frame rates, introducing latency in control. The method uses a frequency-domain cross-correlation framework, transforming event matching into fast Fourier-space operations exceeding 300 Hz. By leveraging binary event frames and image compression, localization accuracy is maintained while computational speed is increased. Experiments with a Prophesee EVK4 HD on an AgileX Scout Mini demonstrate successful navigation over 4000+ meters, achieving ATEs below 24 cm with high-frequency control updates.
Neuromorphic Imaging Flow Cytometry combined with Adaptive Recurrent Spiking Neural Networks
In this paper, an experimental imaging flow cytometer using an event-based CMOS camera is presented, with data processed by adaptive feedforward and recurrent spiking neural networks. PMMA particles flowing in a microfluidic channel are classified, and analysis of experimental data shows that spiking recurrent networks, including LSTM and GRU models, achieve high accuracy by leveraging temporal dependencies. Adaptation mechanisms in lightweight feedforward spiking networks further improve performance. This work provides a roadmap for neuromorphic-assisted biomedical applications, enhancing classification while maintaining low latency and sparsity.
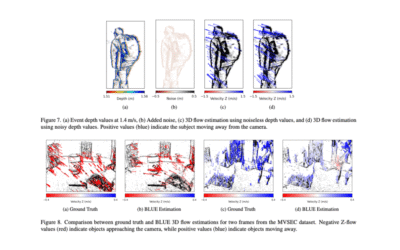
Best Linear Unbiased Estimation for 2D and 3D Flow with Event-based Cameras
In this paper, a novel probabilistic model is proposed that leverages the stochastic distribution of events along moving edges. A lightweight, patch-based algorithm is introduced that employs a linear combination of event spatial coordinates, making it highly suitable for specialized hardware. The approach scales linearly with dimensionality, making it compatible with emerging event-based 3D sensors such as Light-Field DVS (LF-DVS). Experimental results demonstrate the efficiency and scalability of the method, establishing a solid foundation for real-time, ultra-efficient 2D and 3D motion estimation in event-based sensing systems.
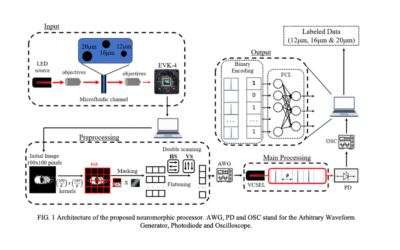
A VCSEL based Photonic Neuromorphic Processor for Event-Based Imaging Flow Cytometry Applications
This paper presents a novel approach that combines a photonic neuromorphic spiking computing scheme with a bio-inspired event-based image sensor. Designed for real-time processing of sparse image data, the system uses a time-delayed spiking extreme learning machine implemented via a two-section laser. Tested on high-flow imaging cytometry data, it classifies artificial particles of varying sizes with 97.1% accuracy while reducing parameters by a factor of 6.25 compared to conventional neural networks. These results highlight the potential of fast, low-power event-based neuromorphic systems for biomedical analysis, environmental monitoring, and smart sensing.
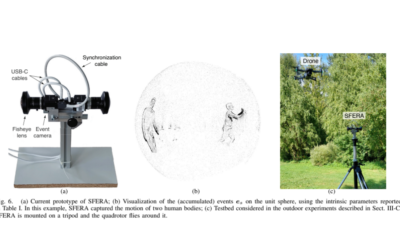
A New Stereo Fisheye Event Camera for Fast Drone Detection and Tracking
In this paper, a new compact vision sensor consisting of two fisheye event cameras mounted back to back is presented, offering a full 360-degree view of the surrounding environment. The optical design, projection model, and practical calibration using incoming event streams of the novel stereo camera called SFERA are described. Its potential for real-time target tracking is evaluated using a Bayesian estimator adapted to the sphere’s geometry. Real-world experiments with a prototype including two synchronized Prophesee EVK4 cameras and a DJI Mavic Air 2 quadrotor demonstrate the system’s effectiveness for aerial surveillance.
Asynchronous Multi-Object Tracking with an Event Camera
In this paper, the Asynchronous Event Multi-Object Tracking (AEMOT) algorithm is presented for detecting and tracking multiple objects by processing individual raw events asynchronously. AEMOT detects salient event blob features by identifying regions of consistent optical flow using a novel Field of Active Flow Directions built from the Surface of Active Events. Detected features are tracked as candidate objects using the recently proposed Asynchronous Event Blob (AEB) tracker to construct small intensity patches of each candidate object.
FRED: The Florence RGB-Event Drone Dataset
The Florence RGB-Event Drone dataset (FRED) is a novel multimodal dataset specifically designed for drone detection, tracking, and trajectory forecasting, combining RGB video and event streams. FRED features more than 7 hours of densely annotated drone trajectories, using five different drone models and including challenging scenarios such as rain and adverse lighting conditions.
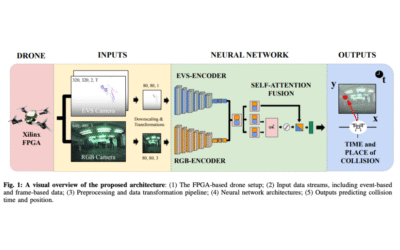
RGB-Event Fusion with Self-Attention for Collision Prediction
This paper proposes a neural network framework for predicting the time and collision position of an unmanned aerial vehicle with a dynamic object, using RGB and event-based vision sensors. The proposed architecture consists of two separate encoder branches, one for each modality, followed by fusion by self-attention to improve prediction accuracy. To facilitate benchmarking, the ABCD dataset is leveraged, enabling detailed comparisons of single-modality and fusion-based approaches.
The neurobench framework for benchmarking neuromorphic computing algorithms and systems
This article presents NeuroBench, a benchmark framework for neuromorphic algorithms and systems. It introduces a common set of tools and systematic methodology for inclusive benchmark measurement, delivering an objective reference framework for quantifying neuromorphic approaches in both hardware-independent and hardware-dependent settings.
Looking into the Shadow: Recording a Total Solar Eclipse with High-resolution Event Cameras
This paper presents the first recording of a total solar eclipse with a pair of high-resolution event cameras, with accompanying methodology. A method is proposed to stabilize the recordings to counteract manual tripod adjustments required to track celestial bodies in-frame. A high-dynamic range image of the sun is also generated during the eclipse, showing how event cameras excel in this aspect compared to traditional CMOS-based cameras.
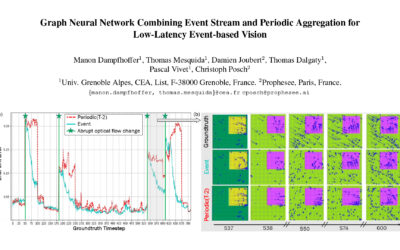
Graph Neural Network Combining Event Stream and Periodic Aggregation for Low-Latency Event-based Vision
This paper proposes a novel architecture combining an asynchronous accumulation-free event branch and a periodic aggregation branch to break the accuracy-latency trade-off. The solution enables ultra low-latency and low-power optical flow prediction from event cameras, achieving per-event prediction with a latency of tens of microseconds.
Evaluation of Commercial-off-the-Shelf Event-Based Cameras for Space Surveillance Applications
The paper evaluates Prophesee’s 3rd-generation event-based cameras for space domain awareness, showing potential for efficient, low-power temporal sensing despite sensitivity limits.
Astrometric Calibration and Source Characterisation of the Latest Generation Neuromorphic Event-based Cameras for Space Imaging
In this paper, the traditional techniques of conventional astronomy are reconsidered to properly utilise the event-based camera for space imaging and space situational awareness.
Motion Segmentation for Neuromorphic Aerial Surveillance
This paper addresses these challenges by introducing a novel motion segmentation method that leverages self-supervised vision transformers on both event data and optical flow information. Our approach eliminates the need for human annotations and reduces dependency on scene-specific parameters.
CoSEC: A Coaxial Stereo Event Camera Dataset for Autonomous Driving
This paper introduces hybrid coaxial event-frame devices to build the multimodal system, and propose a coaxial stereo event camera (CoSEC) dataset for autonomous driving. As for the multimodal system, it first utilizes the microcontroller to achieve time synchronization, and then spatially calibrate different sensors, where they perform intra- and inter-calibration of stereo coaxial devices.
Ev-Layout: A Large-scale Event-based Multi-modal Dataset for Indoor Layout Estimation and Tracking
This paper presents Ev-Layout, a novel large-scale event-based multi-modal dataset designed for indoor layout estimation and tracking. Ev-Layout makes key contributions to the community by: Utilizing a hybrid data collection platform (with a head-mounted display and VR interface) that integrates both RGB and bio-inspired event cameras to capture indoor layouts in motion.
RGBE-Gaze: A Large-Scale Event-Based Multimodal Dataset for High Frequency Remote Gaze Tracking
This paper presents dataset characteristics such as head pose, gaze direction, and pupil size. Furthermore, it introduces a hybrid frame-event based gaze estimation method specifically designed for the collected dataset. Moreover, it performs extensive evaluations of different benchmarking methods under various gaze-related factors.
Synthetic Lunar Terrain: A Multimodal Open Dataset for Training and Evaluating Neuromorphic Vision Algorithms
Synthetic Lunar Terrain (SLT) is an open dataset collected from an analogue test site for lunar missions, featuring synthetic craters in a high-contrast lighting setup. It includes several side-by-side captures from event-based and conventional RGB cameras, supplemented with a high-resolution 3D laser scan for depth estimation.
HUE Dataset: High-Resolution Event and Frame Sequences for Low-Light Vision
Low-light environments pose significant challenges for image enhancement methods. To address these challenges, this work introduces the HUE dataset, a comprehensive collection of high-resolution event and frame sequences captured in diverse and challenging low-light conditions.
M2P2: A Multi-Modal Passive Perception Dataset for Off-Road Mobility in Extreme Low-Light Conditions
Low-light environments pose significant challenges for image enhancement methods. To address these challenges, this work introduces the HUE dataset, a comprehensive collection of high-resolution event and frame sequences captured in diverse and challenging low-light conditions.
eCARLA-scenes: A synthetically generated dataset for event-based optical flow prediction
This papers addresses the lack of datasets by introducing eWiz, a comprehensive library for processing event-based data. It includes tools for data loading, augmentation, visualization, encoding, and generation of training data, along with loss functions and performance metrics.
MouseSIS: A Frames-and-Events Dataset for Space-Time Instance Segmentation of Mice
This paper proposes a novel, computationally efficient regularizer to mitigate event collapse in the CMax framework. From a theoretical point of view, the regularizer is designed based on geometric principles of motion field deformation (measuring area rate of change along point trajectories).
M3ED: Multi-Robot, Multi-Sensor, Multi-Environment Event Dataset
This paper presents M3ED, the first multi-sensor event camera dataset focused on high-speed dynamic motions in robotics applications. M3ED provides high-quality synchronized and labeled data from multiple platforms, including ground vehicles, legged robots, and aerial robots, operating in challenging conditions such as driving along off-road trails, navigating through dense forests, and performing aggressive flight maneuvers.
N-ROD: a Neuromorphic Dataset for Synthetic-to-Real Domain Adaptation
This paper analyzes the synth-to-real domain shift in event data, i.e., the gap arising between simulated events obtained from synthetic renderings and those captured with a real camera on real images.
Real-time event simulation with frame-based cameras
This work proposes simulation methods that improve the performance of event simulation by two orders of magnitude (making them real-time capable) while remaining competitive in the quality assessment.
Object Tracking with an Event Camera
This paper analyzes the synth-to-real domain shift in event data, i.e., the gap arising between simulated events obtained from synthetic renderings and those captured with a real camera on real images.
A Monocular Event-Camera Motion Capture System
This work builds an event-based SL system that consists of a laser point projector and an event camera, and devises a spatial-temporal coding strategy that realizes depth encoding in dual domains through a single shot.
Vision événementielle Omnidirectionnelle : Théorie et Applications
Depuis quelques années, l’utilisation des caméras événementielles est en plein essor en vision par ordinateur et en robotique, et ces capteurs sont à l’origine d’un nombre croissant de projets de recherche portant, par exemple, sur
le véhicule autonome.